2025 Data Breach Forecast and Analysis
Mulayam Yadav
Jan 23, 2025
•
2 Min
Mulayam Yadav
Jan 23, 2025
•
2 Min
As we move towards 2025, global cybersecurity trends reveal that security teams are becoming increasingly adept at detecting and containing data breaches. A persistent cybersecurity skills shortage continues to hinder many organizations, with more than half of breached companies struggling to close the gap. In response, security leaders are leveraging AI-powered solutions and automation tools to enhance incident response and address this deficit. However, despite these efforts, the average cost of a data breach is on the rise.
This blog explores the anticipated trends in data breach costs for 2025 and the key factors driving these changes. It also emphasizes the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures to reduce financial losses and strengthen organizational resilience against future threats.
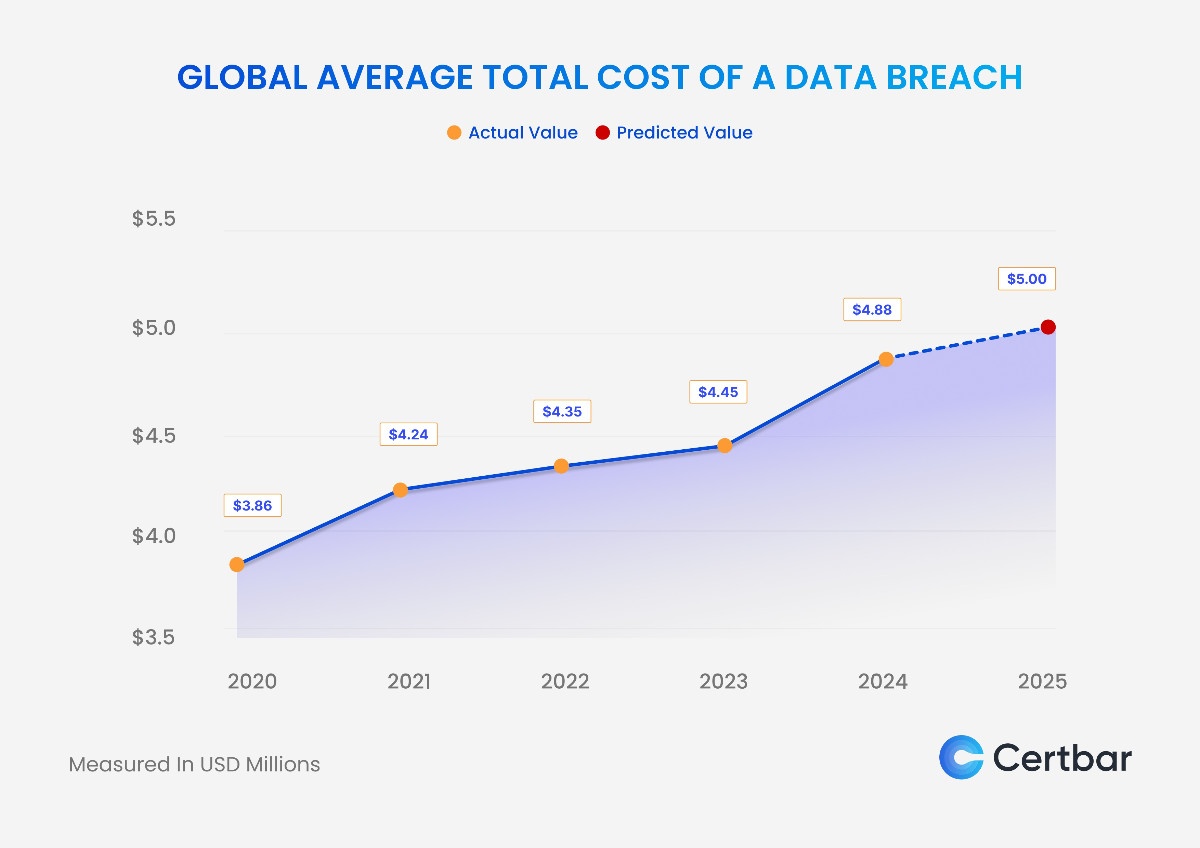
The global average cost of a data breach is projected to reach $5.00 million in 2025, reflecting the growing complexity of cybersecurity risks and operational challenges. The rapid expansion of cloud computing, IoT ecosystems, and hybrid environments has widened the attack surface, making vulnerabilities harder to manage. Attackers are leveraging advanced persistent threats (APTs) and social engineering techniques to launch highly targeted attacks, often bypassing traditional security measures. The increasing volume of sensitive data, from personal information to intellectual property, further amplifies the financial impact, as breaches involving large datasets require extensive remediation and compliance efforts.
In addition, stricter data protection regulations, such as DPDPA-2023, Draft DPDP Rules 2025, GDPR and CCPA, impose significant penalties and reporting obligations, adding to the rising costs. The persistent cybersecurity skills gap exacerbates the problem, as organizations struggle to maintain adequate security operations, leading to longer breach lifecycles. Economic constraints and reliance on outdated systems further hinder efforts to improve resilience. To address these challenges, organizations must adopt zero-trust architecture, enhance incident response planning, and invest in cyber risk management strategies to mitigate the financial and operational impacts of breaches in 2025.
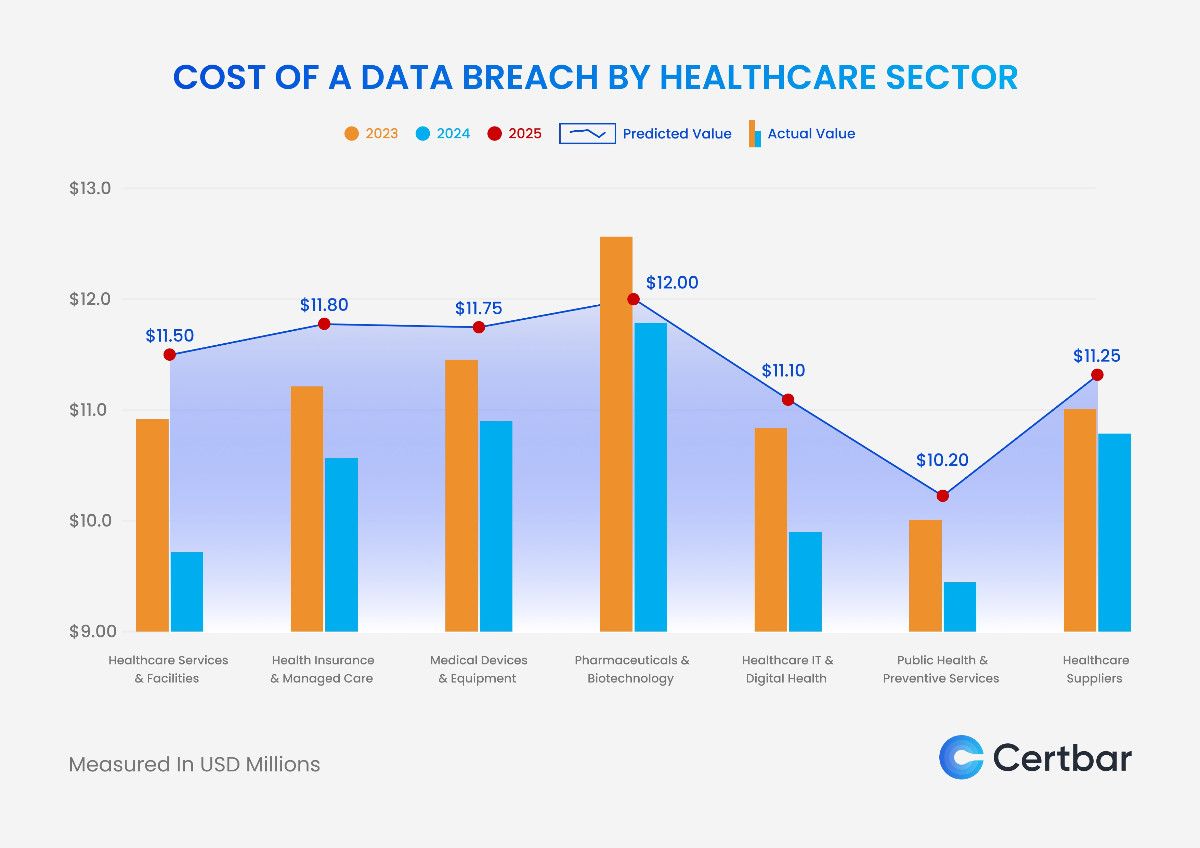
The healthcare industry continues to hold the unenviable position as the costliest sector for data breaches, a trend that has persisted since 2011. Despite advancements in cybersecurity, the industry remains a primary target for attackers due to its reliance on aging technologies, highly sensitive patient data, and the potential for severe operational disruptions.
The healthcare sector is expected to see escalating data breach costs, with some subsectors projected to exceed $12 million in 2025. This chart highlights the varying financial impacts across key areas such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, healthcare IT, and medical devices, reflecting the unique risks anticipated for each subsector.
The rise in costs for 2025 is driven by several factors. Pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, for instance, handle highly sensitive intellectual property and research data, making them prime targets for attackers seeking high-value assets. Substantial costs in healthcare IT and digital health stem from vulnerabilities in hybrid and cloud-based systems that require significant investment in cyber defense to secure. Additionally, medical devices and equipment, now more interconnected than ever, are at higher risk of exploitation due to inadequate security protocols in device ecosystems.
Another contributor to rising breach costs is the regulatory landscape, as healthcare is heavily monitored by data protection frameworks. Compliance failures lead to penalties, while breach notification requirements add to operational and legal expenses. Furthermore, the sector’s reliance on real-time systems and critical infrastructure intensifies the financial burden of downtime, as delays directly impact patient care.
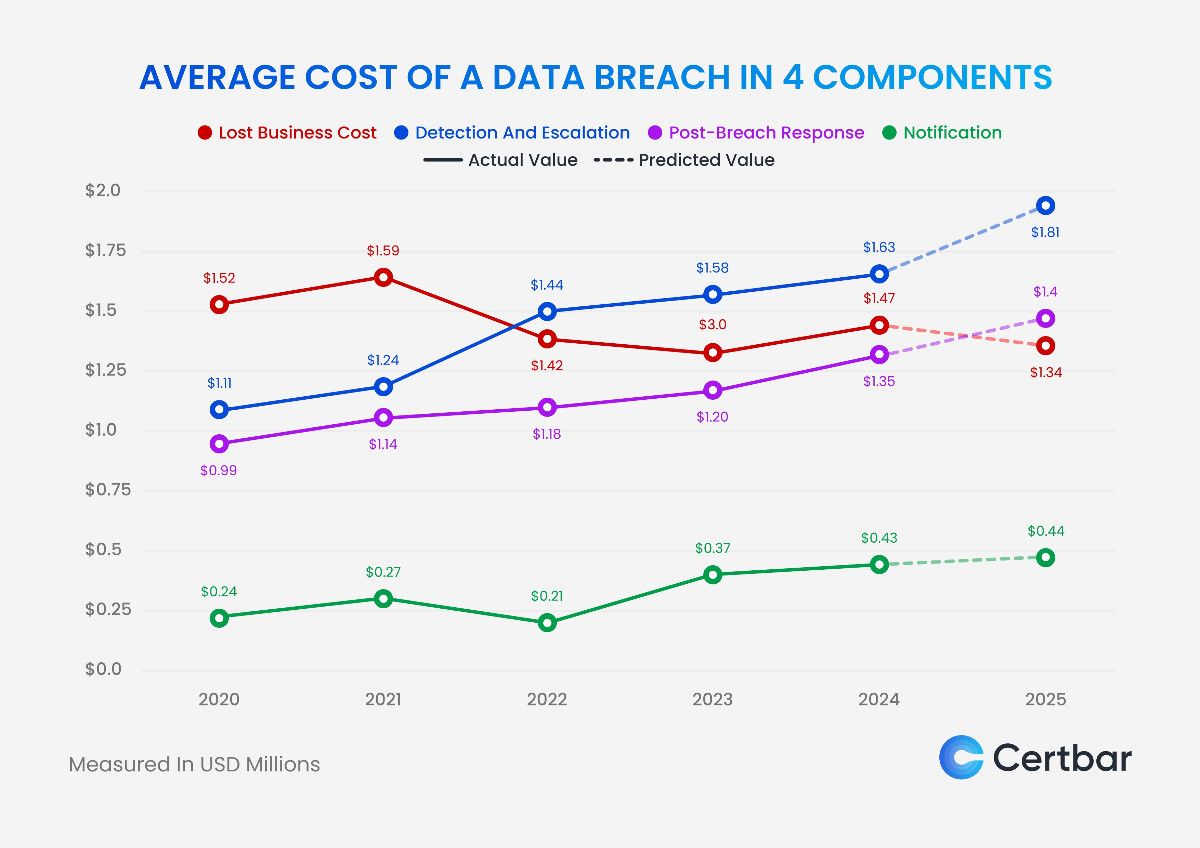
The cost of a data breach is divided into four critical components: lost business, detection and escalation, post-breach response, and notification. Each of these contributes significantly to the overall financial impact of a breach.
The chart illustrates the projected average cost of a data breach in 2025 across four key components: lost business cost, detection and escalation, post-breach response, and notification. Among these, lost business cost remains the highest at $1.34 million, reflecting the financial impact of customer churn, operational downtime, and reputational damage. Detection and escalation costs follow closely, rising to $1.81 million, driven by the need for advanced tools and expertise to investigate breaches. Post-breach response costs, covering legal fees, regulatory fines, and customer remediation, are expected to reach $1.4 million, while notification costs—related to informing affected individuals and regulators—are projected at $0.44 million, reflecting a modest increase.
The rising costs in 2025 can be attributed to multiple factors. The increasing complexity of cyberattacks demands greater investment in breach detection and investigation. Additionally, failure to comply with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA significantly amplifies costs due to hefty fines and increased reporting obligations. For example, organizations that fall short of these standards must allocate more resources for breach remediation, audits, and legal proceedings. The adoption of advanced technologies, such as cloud computing and IoT, has also expanded the attack surface, necessitating more robust cybersecurity defenses. Furthermore, the growing volume of sensitive data in digital ecosystems adds to the costs of containment and response. Lastly, customer expectations for rapid responses and remediation amplify the financial strain, as businesses work to restore trust and minimize brand damage.
The projected rise in data breach costs and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats in 2025 highlight the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity measures. Unpatched vulnerabilities, insecure databases, social engineering, and misconfigured cloud environments remain key drivers, while compliance demands and the cybersecurity skills gap add to the challenges.
Organizations must adopt robust cyber defense frameworks, enhance incident response capabilities, and invest in employee training. Implementing zero-trust architectures, improving compliance with standards like HIPAA and GDPR, and proactively addressing vulnerabilities are crucial to reducing financial and reputational risks.
As a leading cybersecurity provider, we are here to help you secure your organization and stay ahead of emerging threats. To learn more about how we can protect your business, contact us today.
Share