File Integrity Monitoring with YARA
Shreya Dhameliya
Aug 14, 2024
•
13 Min
Shreya Dhameliya
Aug 14, 2024
•
13 Min
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Share
YARA rules can be designed to detect various categories of attacks.
Category | Types of Attack |
Anti-debug/Anti-VM | Anti-analysis techniques to avoid detection. |
Capabilities | Keylogging, network communication, etc. |
Malicious Documents | Macro malware, embedded exploits. |
Crypto | Ransomware, data encryption. |
Phishing, malicious attachments. |
Link:- https://github.com/Yara-Rules/rules?tab=readme-ov-file#capabilities
Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
Processor | Multi-core processor, at least 2 GHz (Intel or AMD). |
Memory (RAM) | Minimum 2 GB for small environments, 4 GB or more recommended for larger environments and to handle intensive YARA scanning. |
Storage | At least 10 GB of free disk space for Wazuh agent installation and log storage. Additional space may be needed based on log retention policies. |
Operating System | Supports Linux, Windows, and Mac OS. |
Network | Stable network connection for communication between Wazuh agents and Wazuh manager. |
Aspect | Wazuh | YARA |
Primary Function | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Intrusion Detection System (IDS). | Malware identification and file scanning using custom rules. |
Role in Monitoring | Monitors directories and files for changes such as creation, modification, or deletion. | Scans files for malware based on custom rules when triggered by Wazuh's FIM module. |
Scanning Mechanism | Uses File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) to detect file changes and generate alerts. | Performs scans based on YARA rules to identify malicious files. |
Trigger Mechanism | Detects changes in monitored directories and files, triggering alerts and active responses. | Activated by Wazuh’s FIM alerts to scan specific files for malware using predefined YARA rules. |
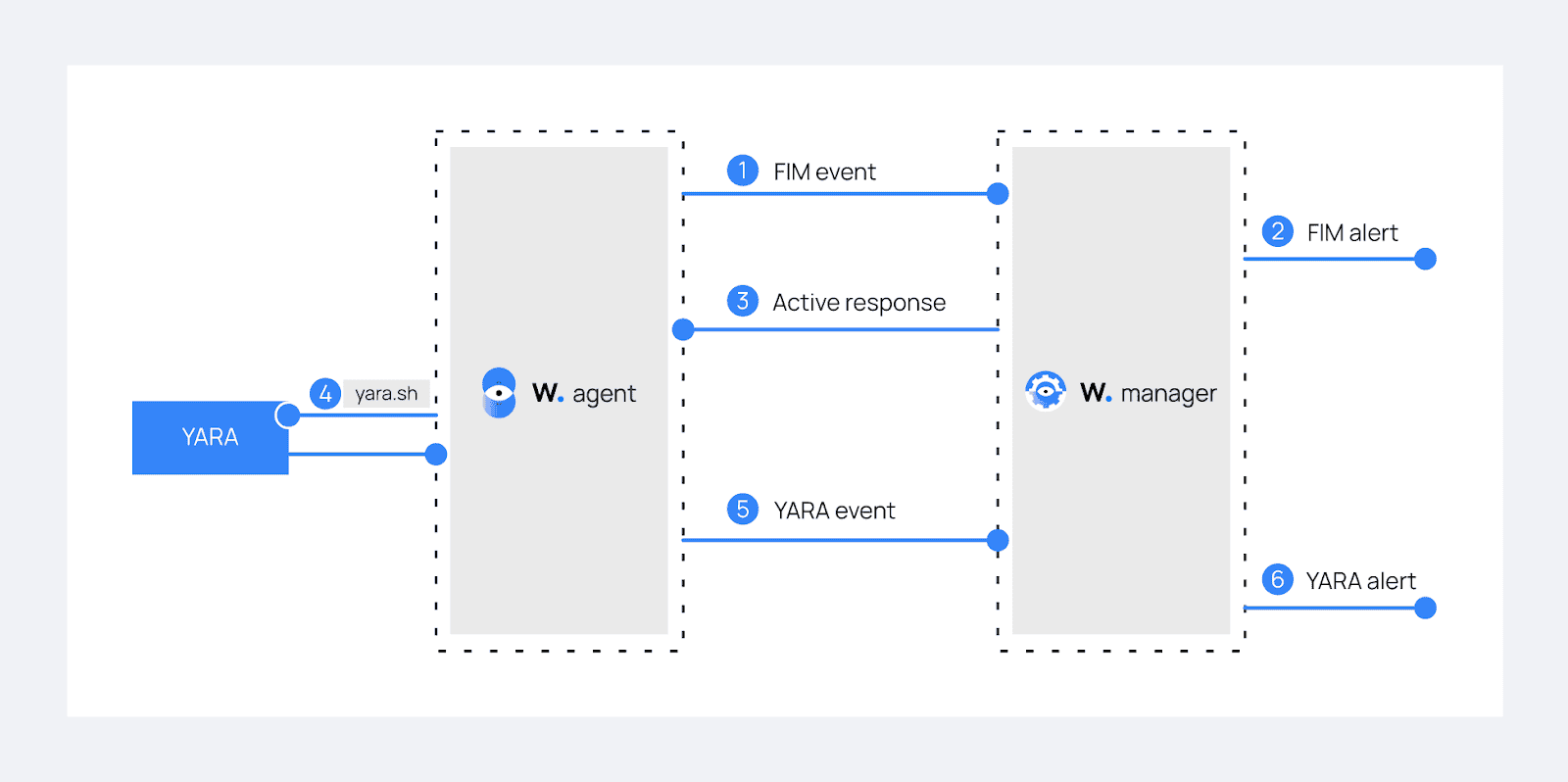
Step: 1 Download, compile and install YARA:
linux Command:-
$sudo apt update
$sudo apt install -y make gcc autoconf libtool libssl-dev pkg-config jq
$sudo curl -LO https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/archive/v4.2.3.tar.gz
$sudo tar -xvzf v4.2.3.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ && rm -f v4.2.3.tar.gz
$cd /usr/local/bin/yara-4.2.3/
$sudo ./bootstrap.sh && sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make install && sudo make checkStep: 2 Test that YARA is running properly:
linux Command:-
$yaraIf the error message below is displayed:
/usr/local/bin/yara: error while loading shared libraries: libyara.so.9: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory.This means that the loader doesn’t find the libyara library usually located in /usr/local/lib. Add the /usr/local/lib path to the /etc/ld.so.conf loader configuration file to solve this:
linux Command:-
$sudo su
$echo "/usr/local/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf
$ldconfigStep: 3 Download YARA detection rules:
linux Command:-
$sudo mkdir -p /tmp/yara/rules
$sudo curl 'https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/api/v1/get' \
-H 'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8' \
-H 'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5' \
--compressed \
-H 'Referer: https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
-H 'DNT: 1' -H 'Connection: keep-alive' -H 'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1' \
--data 'demo=demo&apikey=1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111&format=text' \
-o /tmp/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar
Step: 4 Create a yara.sh script in the /var/ossec/active-response/bin/ directory. This is necessary for the Wazuh-YARA active response scans:
#!/bin/bash
# Wazuh - Yara active response
# Copyright (C) 2015-2022, Wazuh Inc.
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it
# and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
# License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software
# Foundation.
#------------------------- Gather parameters -------------------------#
# Extra arguments
read INPUT_JSON
YARA_PATH=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[1])
YARA_RULES=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[3])
FILENAME=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.alert.syscheck.path)
# Set LOG_FILE path
LOG_FILE="logs/active-responses.log"
size=0
actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME})
while [ ${size} -ne ${actual_size} ]; do
sleep 1
size=${actual_size}
actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME})
done
#----------------------- Analyze parameters -----------------------#
if [[ ! $YARA_PATH ]] || [[ ! $YARA_RULES ]]
then
echo "wazuh-yara: ERROR - Yara active response error. Yara path and rules parameters are mandatory." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
#------------------------- Main workflow --------------------------#
# Execute Yara scan on the specified filename
yara_output="$("${YARA_PATH}"/yara -w -r "$YARA_RULES" "$FILENAME")"
if [[ $yara_output != "" ]]
then
# Iterate every detected rule and append it to the LOG_FILE
while read -r line; do
echo "wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: $line" >> ${LOG_FILE}
done <<< "$yara_output"
fi
exit 0;Step: 5. Change yara.sh file owner to root:wazuh and file permissions to 0750:
linux Command:-
$sudo chown root:wazuh /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh
$sudo chmod 750 /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh
Step: 6 Add the following within the <syscheck> block of the Wazuh agent /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf configuration file to monitor the /tmp/yara/malware directory:
<directories realtime="yes">/tmp/yara/malware</directories>
<directories realtime="yes">/tmp/quarantined/</directories>Step: 7 Restart the Wazuh agent to apply the configuration changes:
linux Command:-
$sudo systemctl restart wazuh-agent
Step: 1 Add the following rules to the /var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xml file. The rules detect FIM events in the monitored directory. They also alert when the YARA integration finds malware. You can modify the rules to detect events from other directories:
<group name="syscheck,">
<rule id="100300" level="7">
<if_sid>550</if_sid>
<field name="file">/tmp/yara/malware/</field>
<description>File modified in /tmp/yara/malware/ directory.</description>
</rule>
<rule id="100301" level="7">
<if_sid>554</if_sid>
<field name="file">/tmp/yara/malware/</field>
<description>File added to /tmp/yara/malware/ directory.</description>
</rule>
<rule id="100302" level="7">
<if_sid>550</if_sid>
<field name="file">/tmp/quarantined/</field>
<description>Malicious File modified in /tmp/quarantined/ directory.</description>
</rule>
<rule id="100303" level="7">
<if_sid>554</if_sid>
<field name="file">/tmp/quarantined/</field>
<description>Malicious File added to /tmp/quarantined/ directory.</description>
</rule>
</group>
<group name="yara,">
<rule id="108000" level="0">
<decoded_as>yara_decoder</decoded_as>
<description>Yara grouping rule</description>
</rule>
<rule id="108001" level="12">
<if_sid>108000</if_sid>
<match>wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: </match>
<description>File "$(yara_scanned_file)" is a positive match. Yara rule: $(yara_rule)</description>
</rule>
</group>Step: 2 Add the following decoders to the Wazuh server /var/ossec/etc/decoders/local_decoder.xml file. This allows extracting the information from YARA scan results:
<decoder name="yara_decoder">
<prematch>wazuh-yara:</prematch>
</decoder>
<decoder name="yara_decoder1">
<parent>yara_decoder</parent>
<regex>wazuh-yara: (\S+) - Scan result: (\S+) (\S+)</regex>
<order>log_type, yara_rule, yara_scanned_file</order>
</decoder>Step: 3 Add the following configuration to the Wazuh server /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf configuration file. This configures the active response module to trigger after the rule 100300 and 100301 are fired:
<ossec_config>
<command>
<name>yara_linux</name>
<executable>yara.sh</executable>
<extra_args>-yara_path /usr/local/bin -yara_rules /tmp/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar</extra_args>
<timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed>
</command>
<active-response>
<command>yara_linux</command>
<location>local</location>
<rules_id>100300,100301</rules_id>
</active-response>
</ossec_config>Step: 4 Restart the Wazuh manager to apply the configuration changes:
linux Command:-
$sudo systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Step: 1 Create the script /tmp/yara/malware/malware_downloader.sh on the monitored endpoint to download malware samples:
#!/bin/bash
# Wazuh - Malware Downloader for test purposes
# Copyright (C) 2015-2022, Wazuh Inc.
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it
# and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
# License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software
# Foundation.
function fetch_sample(){
curl -s -XGET "$1" -o "$2"
}
echo "WARNING: Downloading Malware samples, please use this script with caution."
read -p " Do you want to continue? (y/n)" -n 1 -r ANSWER
echo
if [[ $ANSWER =~ ^[Yy]$ ]]
then
echo
# Mirai
echo "# Mirai: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mirai_(malware)"
echo "Downloading malware sample..."
fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/mirai" "/tmp/yara/malware/mirai" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading."
echo
# Xbash
echo "# Xbash: https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/unit42-xbash-combines-botnet-ransomware-coinmining-worm-targets-linux-windows/"
echo "Downloading malware sample..."
fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/xbash" "/tmp/yara/malware/xbash" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading."
echo
# VPNFilter
echo "# VPNFilter: https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2018/05/24/vpnfilter-botnet-a-sophoslabs-analysis/"
echo "Downloading malware sample..."
fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/vpn_filter" "/tmp/yara/malware/vpn_filter" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading."
echo
# Webshell
echo "# WebShell: https://github.com/SecWiki/WebShell-2/blob/master/Php/Worse%20Linux%20Shell.php"
echo "Downloading malware sample..."
fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/webshell" "/tmp/yara/malware/webshell" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading."
echo
fiStep: 2 Run the malware_downloader.sh script to download malware samples to the /tmp/yara/malware directory:
linux Command:-
$sudo bash /tmp/yara/malware/malware_downloader.sh
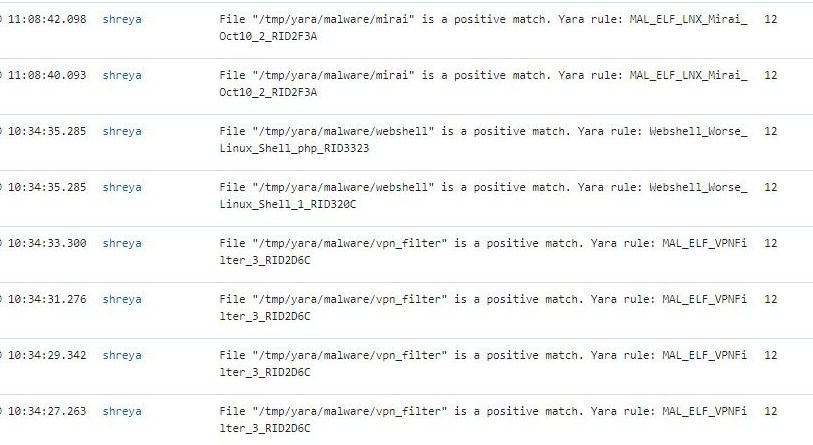
This is a modified version of the script, now integrated into the active response on the Wazuh agent side. It includes a quarantine feature that moves detected files to a specified directory. By default, the directory used is /tmp/quarantined. Before running the script, ensure this directory is created, or feel free to modify the path to one of your choosing.
/tmp/quarantined nano /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh #!/bin/bash
# Wazuh - Yara active response
# Copyright (C) 2015-2022, Wazuh Inc.
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it
# and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
# License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software
# Foundation.
#------------------------- Gather parameters -------------------------#
# Extra arguments
read INPUT_JSON
YARA_PATH=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[1])
YARA_RULES=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[3])
FILENAME=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.alert.syscheck.path)
# Set LOG_FILE path
LOG_FILE="logs/active-responses.log"
# Set quarantine directory
QUARANTINE_DIR="/tmp/quarantined"
# Ensure quarantine directory exists
mkdir -p "$QUARANTINE_DIR"
size=0
actual_size=$(stat -c %s "$FILENAME")
while [ ${size} -ne ${actual_size} ]; do
sleep 1
size=${actual_size}
actual_size=$(stat -c %s "$FILENAME")
done
#----------------------- Analyze parameters -----------------------#
if [[ ! $YARA_PATH ]] || [[ ! $YARA_RULES ]]
then
echo "wazuh-yara: ERROR - Yara active response error. Yara path and rules parameters are mandatory." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
#------------------------- Main workflow --------------------------#
# Execute Yara scan on the specified filename
yara_output="$("${YARA_PATH}"/yara -w -r "$YARA_RULES" "$FILENAME")"
# If Yara rules are triggered, move file to quarantine directory
if [[ -n $yara_output ]]
then
# Iterate every detected rule and append it to the LOG_FILE
while read -r line; do
echo "wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: $line" >> ${LOG_FILE}
done <<< "$yara_output"
# Move the file to quarantine directory
mv "$FILENAME" "${QUARANTINE_DIR}/$(basename "$FILENAME")"
echo "wazuh-yara: INFO - File quarantined: ${FILENAME}" >> ${LOG_FILE}
fi
exit 0;
Perform the following steps to install Python, YARA, and download YARA rules.
Step: 1 Download Python executable installer from the official Python website.
Step: 2 Run the Python installer once downloaded and make sure to check the following boxes:
Step: 3 Download and install the latest Visual C++ Redistributable package.
Step: 4 Open PowerShell with administrator privileges to download and extract YARA:
Python Command:-
> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/releases/download/v4.2.3/yara-4.2.3-2029-win64.zip -OutFile v4.2.3-2029-win64.zip
> Expand-Archive v4.2.3-2029-win64.zip; Remove-Item v4.2.3-2029-win64.zipStep: 5 Create a directory called C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\ and copy the YARA executable into it:
Python Command:-
> mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\'
> cp .\v4.2.3-2029-win64\yara64.exe 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\'
Step: 6 Install the valhallaAPI module:
Python Command:-
> pip install valhallaAPIStep:7 Copy the following script and save it as download_yara_rules.py:
from valhallaAPI.valhalla import ValhallaAPI
v = ValhallaAPI(api_key="1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111")
response = v.get_rules_text()
with open('yara_rules.yar', 'w') as fh:
fh.write(response)Step: 8 Run the following commands to download the rules and place them in the C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\ directory:
Python Command:-
> python.exe download_yara_rules.py
> mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\'
> cp yara_rules.yar 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\'
Perform the steps below to configure the Wazuh FIM and an active response script for the detection of malicious files on the endpoint.
Step: 1 Create the yara.bat script in the C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\ directory. This is necessary for the Wazuh-YARA active response scans:
@echo off
setlocal enableDelayedExpansion
reg Query "HKLM\Hardware\Description\System\CentralProcessor\0" | find /i "x86" > NUL && SET OS=32BIT || SET OS=64BIT
if %OS%==32BIT (
SET log_file_path="%programfiles%\ossec-agent\active-response\active-responses.log"
)
if %OS%==64BIT (
SET log_file_path="%programfiles(x86)%\ossec-agent\active-response\active-responses.log"
)
set input=
for /f "delims=" %%a in ('PowerShell -command "$logInput = Read-Host; Write-Output $logInput"') do (
set input=%%a
)
set json_file_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\stdin.txt"
set syscheck_file_path=
echo %input% > %json_file_path%
for /F "tokens=* USEBACKQ" %%F in (`Powershell -Nop -C "(Get-Content 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\stdin.txt'|ConvertFrom-Json).parameters.alert.syscheck.path"`) do (
set syscheck_file_path=%%F
)
del /f %json_file_path%
set yara_exe_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\yara64.exe"
set yara_rules_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\yara_rules.yar"
echo %syscheck_file_path% >> %log_file_path%
for /f "delims=" %%a in ('powershell -command "& \"%yara_exe_path%\" \"%yara_rules_path%\" \"%syscheck_file_path%\""') do (
echo wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: %%a >> %log_file_path%
)
exit /b
Step: 2 Add the C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads directory for monitoring within the <syscheck> block in the Wazuh agent configuration file C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\ossec.conf. Replace <USER_NAME> with the username of the endpoint:
<directories realtime="yes">C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads</directories>Step: 3 Restart the Wazuh agent to apply the configuration changes:
Python Command:-
> Restart-Service -Name wazuh
Perform the following steps on the Wazuh server. This allows alerting for changes in the endpoint monitored directory and configuring an active response script to trigger whenever it detects a suspicious file.
Step: 1 Add the following decoders to the Wazuh server /var/ossec/etc/decoders/local_decoder.xml file. This allows extracting the information from YARA scan results:
<decoder name="yara_decoder">
<prematch>wazuh-yara:</prematch>
</decoder>
<decoder name="yara_decoder1">
<parent>yara_decoder</parent>
<regex>wazuh-yara: (\S+) - Scan result: (\S+) (\S+)</regex>
<order>log_type, yara_rule, yara_scanned_file</order>
</decoder>Step: 2 Add the following rules to the Wazuh server /var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xml file. The rules detect FIM events in the monitored directory. They also alert when malware is found by the YARA integration:
<group name="syscheck,">
<rule id="100303" level="7">
<if_sid>550</if_sid>
<field name="file">C:\\Users\\<USER_NAME>\\Downloads</field>
<description>File modified in C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads directory.</description>
</rule>
<rule id="100304" level="7">
<if_sid>554</if_sid>
<field name="file">C:\\Users\\<USER_NAME>\\Downloads</field>
<description>File added to C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads directory.</description>
</rule>
</group>
<group name="yara,">
<rule id="108000" level="0">
<decoded_as>yara_decoder</decoded_as>
<description>Yara grouping rule</description>
</rule>
<rule id="108001" level="12">
<if_sid>108000</if_sid>
<match>wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: </match>
<description>File "$(yara_scanned_file)" is a positive match. Yara rule: $(yara_rule)</description>
</rule>
</group>Step: 3 Add the following configuration to the Wazuh server /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf file:
<ossec_config>
<command>
<name>yara_windows</name>
<executable>yara.bat</executable>
<timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed>
</command>
<active-response>
<command>yara_windows</command>
<location>all</location>
<rules_id>100303,100304</rules_id>
</active-response>
</ossec_config>Step: 4 Restart the Wazuh manager to apply the configuration changes:
Command:-
$sudo systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Download a malware sample on the monitored Windows endpoint:
Step: 1 Turn off Microsoft Virus and threat protection.
Step: 2 Download the EICAR zip file:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://secure.eicar.org/eicar_com.zip -OutFile eicar.zipStep: 3 Unzip it:
Python Command:-
> Expand-Archive .\eicar.zipStep: 4 Copy the EICAR file to the monitored directory:
Python Command:-
> cp .\eicar\eicar.com C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads

In conclusion, integrating YARA with Wazuh significantly enhances your security posture by enabling advanced malware detection through custom rules. By leveraging Wazuh’s File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) and YARA’s powerful pattern-matching capabilities, you can effectively monitor and respond to potential threats across both Linux and Windows environments. The combination of these tools allows for a proactive approach to cybersecurity, ensuring that your systems are continuously monitored and protected against a wide range of malicious activities. Whether you're a security professional or a system administrator, the steps outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for implementing YARA and Wazuh in your security strategy, enabling you to stay ahead of emerging threats.

Share